Cornea Of The Eye Cornea Definition 10-foods-highest-in-iron. The cornea is the unmistakable front surface of the eye. It lies straightforwardly before the iris and student, and it permits light to enter the eye. Seen from the front of the eye, the cornea shows up marginally more extensive than it is tall. This is on the grounds that the sclera (the "white" of the eye) somewhat covers the top and lower part of the front cornea. The level distance across of the cornea normally gauges around 12 millimeters (mm), and the upward breadth is 11 mm, when seen from the front. However, whenever saw from behind, the cornea seems roundabout, with a uniform measurement of around 11.7 mm. This makes the cornea around 66% the size of a dime. The middle thickness of the normal cornea is around 550 microns, or somewhat the greater part a millimeter. The cornea has five layers. From front to back, these layers are: The corneal epithelium. This external layer of the cornea is five to se...
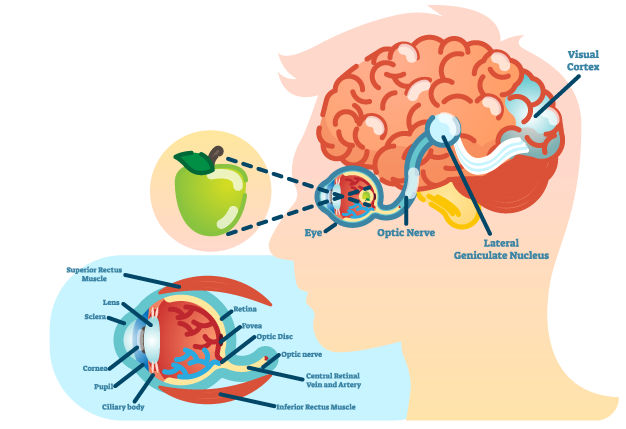
The Retina: Where Vision Begins
Retina Definition
The retina is the sensitive layer that covers the inner surface of the back of the eye. It consists of several layers, with one layer containing specialized cells known as photoreceptors.
The natural eye contains two types of photoreceptor cells - rods and cones.
Rod photoreceptors detect motion, provide high-contrast vision, and function effectively in dim lighting. Cones are responsible for central vision and color perception, functioning optimally in moderate to bright lighting.
Rods are distributed throughout the retina; cones are concentrated in a small central area of the retina known as the macula. At the center of the macula lies a small depression known as the fovea. The fovea has only cone photoreceptors and is the area in the retina responsible for maximum visual clarity and color perception.
Retinal Function
Photoreceptor cells capture light focused by the cornea and lens, transforming it into chemical and electrical signals that are transmitted to visual areas in the brain through the optic nerve. [Refer to eye illustration.]
In the cerebrum's visual cortex (located at the back of the brain, by the way), these signals are converted into images and visual perceptions.
Problemas de Retina
There is a broad variety of retinal issues and diseases. Here is an overview of the typical retina:
Degeneration of the macula. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most commonly acknowledged serious, age-related eye condition, affecting 9.1 million individuals in the United States. Additionally, the prevalence of AMD - which affects one in 14 Americans over 40 and more than 30% of those over 75 - is rising as the U.S. population continues to age.
Retinopathy in diabetes.
A significant result of diabetes is damage to the blood vessels that supply and nourish the retina, leading to severe vision loss.
Macular edema.
This is a gathering of liquid and expanding of the macula, causing contortion and obscured focal vision. Macular edema has a few causes, including diabetes. At times, expanding of the macula can happen after waterfall medical procedure.
Focal serous retinopathy.
This is when liquid develops under the focal retina, causing misshaped vision. However the reason for focal serous retinopathy (CSR) regularly is obscure, it will in general influence men in their 30s to 50s more every now and again than ladies, and stress seems, by all accounts, to be a significant gamble factor.
Hypertensive retinopathy.
Ongoing hypertension can harm the little veins that support the retina, prompting critical vision issues. Risk factors for hypertensive retinopathy are equivalent to those for hypertension, including heftiness, absence of actual work, eating an excess of salt, a family background of hypertension and an unpleasant way of life.
Sun based retinopathy.
This is harm to the macula from gazing at the sun, which can cause a super durable vulnerable side (scotoma) in your visual field. The gamble of sunlight based retinopathy (likewise called sun oriented maculopathy) is most noteworthy while review a sun powered overshadow without satisfactory eye assurance. [Read about how to safeguard your eyes during a sunlight based eclipse.]
Separated retina.
A retinal separation - a pulling away of the retina from the basic choroid layer of the eye that gives its sustenance - is a health related crisis. On the off chance that the retina isn't carefully reattached quickly, long-lasting and deteriorating vision misfortune can happen.
The Retina: Where Vision Begins VIDEO
Comments
Post a Comment